[Coding046] LeetCode 388
Longest Absolute File Path
Get the knowledge flowing and circulating! :)
目录
※ 本题收获
不能囿于某一特定的数据结构,我在做这道题的时候,老是想着用栈来解决,殊不知把自己的解法固定在了一个狭小的空间里,忽略了明显的提示:文件的树型结构。
收获最大的还是思想(十分巧妙的hashmap使用,让文件之间的层次关系得以突显。)
xxxxxxxxxx11hashmap.put(level + 1, hashmap.get(level) + len + 1);hashmap.put(level + 1, ...)hashmap.get(level) + ...这两句代码将层与层之间的关系联接了起来。十分巧妙!
题目:388. Longest Absolute File Path
Suppose we have a file system that stores both files and directories. An example of one system is represented in the following picture:
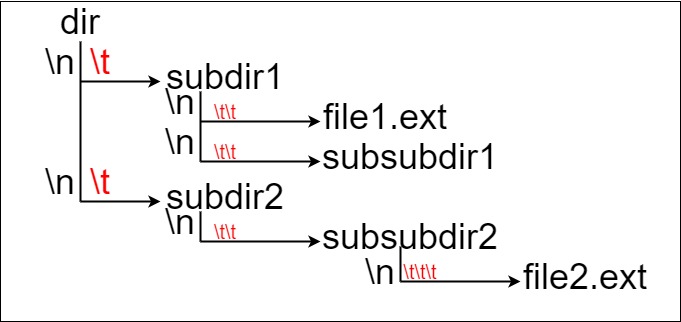
Here, we have dir as the only directory in the root. dir contains two subdirectories, subdir1 and subdir2. subdir1 contains a file file1.ext and subdirectory subsubdir1. subdir2 contains a subdirectory subsubdir2, which contains a file file2.ext.
In text form, it looks like this (with ⟶ representing the tab character):
xxxxxxxxxx71dir2⟶ subdir13⟶ ⟶ file1.ext4⟶ ⟶ subsubdir15⟶ subdir26⟶ ⟶ subsubdir27⟶ ⟶ ⟶ file2.ext
If we were to write this representation in code, it will look like this: "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext". Note that the '\n' and '\t' are the new-line and tab characters.
Every file and directory has a unique absolute path in the file system, which is the order of directories that must be opened to reach the file/directory itself, all concatenated by '/'s. Using the above example, the absolute path to file2.ext is "dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext". Each directory name consists of letters, digits, and/or spaces. Each file name is of the form name.extension, where name and extension consist of letters, digits, and/or spaces.
Given a string input representing the file system in the explained format, return the length of the longest absolute path to a file in the abstracted file system. If there is no file in the system, return 0.
Note that the testcases are generated such that the file system is valid and no file or directory name has length 0.
Example 1:
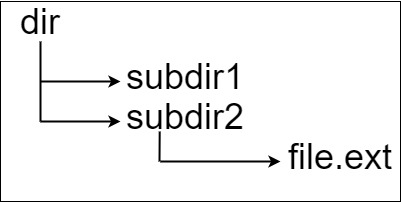
xxxxxxxxxx31Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext"2Output: 203Explanation: We have only one file, and the absolute path is "dir/subdir2/file.ext" of length 20.
Example 2:
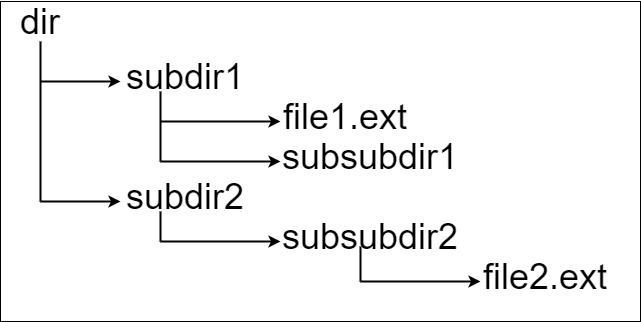
xxxxxxxxxx61Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext"2Output: 323Explanation: We have two files:4"dir/subdir1/file1.ext" of length 215"dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext" of length 32.6We return 32 since it is the longest absolute path to a file.
Example 3:
xxxxxxxxxx31Input: input = "a"2Output: 03Explanation: We do not have any files, just a single directory named "a".
Constraints:
1 <= input.length <= 104inputmay contain lowercase or uppercase English letters, a new line character'\n', a tab character'\t', a dot'.', a space' ', and digits.All file and directory names have positive length.
代码1(配 · 手绘过程图)Wrong
xxxxxxxxxx1161class Solution {2 public int lengthLongestPath(String input) {3 4 String[] seg = input.split("\n");5
6 String[] files = new String[1000];7 int[] tCnt = new int[1000];8
9 int i = 0;10
11 for(String each : seg)12 {13 // System.out.println("-->" + each);14 String[] seg2 = each.split("\t");15 for(String xx : seg2)16 {17 System.out.println("====>" + xx);18 if (xx == "")19 {20 System.out.println("line20");21 tCnt[i]++;22 continue;23 }24 else25 { 26 System.out.println("line25");27 files[i] = xx;28 }29 i++;30 }31 }32
33 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)34 {35 System.out.println("++++>" + tCnt[j] + " | " + files[j]);36 }37 38 // 到此的想法是:用'\t'的数量来控制出栈、入栈的情况;39 /*40 ++++>0 | dir41 ++++>1 | subdir142 ++++>2 | file1.ext43 ++++>2 | subsubdir144 ++++>1 | subdir245 ++++>2 | subsubdir246 ++++>3 | file2.ext47 */48
49 // 但是到这里的时候,出栈入栈的思路是对的,实现起来略微复杂,遂弃之。50 Stack<String> st = new Stack();51 int max = 0;52
53 st.push(files[0]);54 int curT = 0;55 max = max + files[0].length() + 1;56 for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)57 {58 if (tCnt[j] > curT)59 {60 curT = tCnt[j];61 st.push(files[j]);62 if (files[j].contains("."))63 {64 max = max + st.peek().length();65 }66 else67 {68 max = max + st.peek().length() + 1;;69 }70 }71 else if (tCnt[j] == curT)72 {73 if (st.peek().contains("."))74 {75 max = max - st.pop().length();76 }77 else78 {79 max = max - st.pop().length() - 1;80 }81 st.push(files[j]);82 if (files[j].contains("."))83 {84 max = max + st.peek().length();85 }86 else87 {88 max = max + st.peek().length() + 1;;89 }90 }91 else92 {93 if (st.peek().contains("."))94 {95 max = max - st.pop().length();96 }97 else98 {99 max = max - st.pop().length() - 1;100 }101 curT = tCnt[j];102 st.push(files[j]);103 if (files[j].contains("."))104 {105 max = max + st.peek().length();106 }107 else108 {109 max = max + st.peek().length() + 1;;110 }111 }112 }113
114 return max;115 }116}
代码解读 | 评价
这段代码囿于“栈”的思维,忽略了明显的提示:文件的树形结构。
虽然用栈可以做出来,但是思维略微复杂。
代码2(配 · 手绘过程图)
xxxxxxxxxx331class Solution {2 public int lengthLongestPath(String input) {3 4 HashMap<Integer, Integer> hashmap = new HashMap<>();5 hashmap.put(0, 0);6
7 int maxLen = 0;8
9 String[] eachPath = input.split("\n");10
11 for (String s : eachPath)12 {13 // 因为'\t'在字符串中,是一个转义字符,所以算1个字符14 // 计算方法很巧妙:因为'\t'都是在每个s的最前面,所以最后一次出现的'\t'的位置 + 1就是它的个数15 int level = s.lastIndexOf('\t') + 1; // 计算单个字符'\t'的个数16
17 // 要减掉'\t'的个数,因为最后累加到maxLen里的是纯路径名/文件名,没有'\t'18 int len = s.length() - level;19
20 if (s.contains("."))21 {22 maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, hashmap.get(level) + len);23 }24 else25 {26 hashmap.put(level + 1, hashmap.get(level) + len + 1); // value中的尾巴1是路径中'/'27 }28
29 }30
31 return maxLen;32 }33}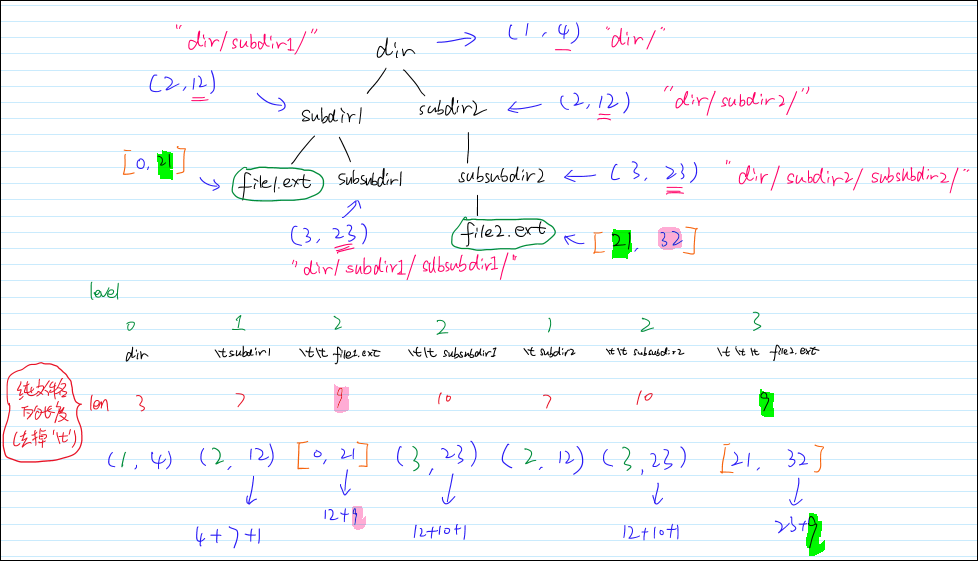
代码解读 | 评价
非常巧妙的代码!
利用了树形结构的特点,思路更加清晰。
★ 知识点积累 (Java)
HashMap的基本用法(
get()&put())计算转义字符的个数(巧妙方法):
lastIndexOf('\t') + 1字符串中是否包括某个字符串的方法:
contains()